High Power Ultra-Low-Ohmic Shunt Resistors 5W class
ROHM High Power Ultra-Low-Ohmic Shunt Resistors 5W class, ideal for current detection in automotive and industrial application
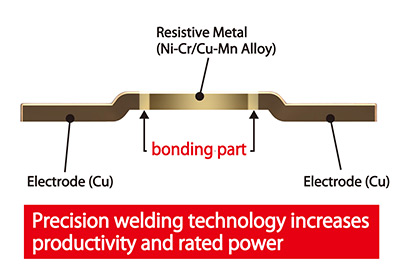
ROHM has recently announced the development of high power ultra-low-ohmic shunt resistors ideal for current detection in applications with increased power requirements, such as automotive systems and industrial equipment. The new PSR series includes PSR400, which is rated at 4W, and PSR500, guaranteed up to 5W, while a high-performance alloy was adopted in the resistive metal for superior TCR in the low-ohmic region. This ensures sufficient margin even in applications with stringent temperature requirements, such as automotive systems and industrial equipment, while lightening design load.
Key Features:
- Exclusive precision welding technology utilized for improved rated power (5W)
- Superior temperature coefficient of resistance, even in the ultra-low-ohmic region
- as resistance value decreases the temperature coefficient of resistance increases.
- utilization of high-performance alloy material for the resistive metal, ensuring superior temperature coefficient of resistance even at ultra-low resistances
Terminology:
TCR (Temperature Coefficient of Resistance) The lower this value is the smaller the change in resistance value in response to changes in ambient temperature, making it possible to suppress variations in device operation.
To access the product datasheet on the Rohm Website, go to http://rohmfs.rohm.com/en/products/databook/datasheet/passive/resistor/chip_resistor/psr.pdf