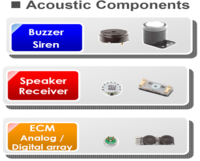
Resonators, Acoustics, Filters
Piezoelectric Effect
The Piezoelectric Effect is understood as the linear electromechanical interaction between the mechanical and the electrical state in crystalline materials with no inversion symmetry. This effect is a reversible process in that materials exhibiting the direct Piezoelectric Effect (electrical charge resulting from an applied mechanical force) and the reverse Piezoelectric Effect (mechanical strain resulting from an applied electrical field). Piezoelectricity is found in applications such as the production and detection of sound, generation of high voltages or electronic frequency generation.
Ceramic Resonators
Ceramic Resonators are made of high stability piezoelectric ceramics with the same function as a mechanical resonator. Resonators can be used as the timing element in most microprocessor based equipment.
Ceramic Filters
Ceramic Filters derive their basic frequency selectivity from a mechanical vibration resulting from a Piezoelectric Effect. Normally all low and high-end AM/FM commercial radios use ceramic bandpass filters. However, Ceramic Filters are also applied in Car Audio Systems, wireless applications/modules, Remote Controls, Automotive and Industry.
Speaker
A speaker is made for producing sound waves, generated by rapidly vibrating a flexible cone, or membrane. The cone is attached on the wide end to the suspension and usually made of paper, plastic or metal. In general speakers produce a much higher sound pressure also in low frequencies. Microspeakers are magnetic speakers as well, but their size is compact and for this reason often used for headphones and tiny applications.
Piezo Buzzer
Piezoelectric Speakers, comparable with Electrodynamic Speakers, are characterized by an alternating voltage on piezoceramic. The alternating contraction and expansion of piezoceramic set the disc in motion. The frequency response of piezoelectric material is limited, particularly at the lower end and therefore used for higher frequencies.
Magnetic Buzzer
Electrodynamic Speakers are characterized by an alternating magnetic field. The magnetic field interacts of a permanent magnet and produces sound waves which set the cone in motion.
Microphones
Microphones convert sound waves to electrical signals. Electret condenser microphones consist of a very light diaphragm and back plate which is stimulated by a polarizing voltage. Arising sound waves impacting on the light diaphragm cause capacitance between the diaphragm and the back plate. This induces a voltage change on the back plate.
Dynamic Receivers/Microphones are built up in the same way as Speaker with a voice coil but specifically developed for Telecom, Audio and Automotive applications, characterized by a high quality and a wideband range.