ASSMANN WSW – Thermal Management Solutions for LED Lighting Technology
Thermal management and LED lighting technology?
Is there any need for a LED lighting system to think about thermal management, although a
light emitting diode uses much less power, than a standard lamp with an identical light
efficiency?
Referring to this question, there is a clear consent, that there is still a demand for thermal
management. The reason is that a light-emitting diode is nothing else as any other
semiconductor device. Based on the current rating needed, the diode converts up to 70% of the
incoming energy into heat and only 30% into light. Compared with a standard lamp, which is
heat-resistant, an LED generates so much heat without the appropriate thermal management,
that it has a negative impact on their lifetime, the color spectrum and the light efficiency. A
30W standard lamp has much higher energy consumption and compared with a 5W LED light,
based on an identical light efficiency, it acts like a heater. An LED has also the characteristic to
conduct the thermal convection (heat radiation in the infrared range) contrary to the direction
of the light, from the semiconductor crystal back to the PC-Board. That is the reason, why you
detect, that only a very small part of generated heat can be measured at the light itself. Despite
this fact, a 5Watt LED has a comparable power density like a 1KW hotplate.

Figure 1
Figure 2
This means, it is absolutely important to pay special attention at the beginning of the design to
the thermal performance. To cool down LEDs, there are several alternatives available. This can
be reached by the LED housing itself, just by the PCB or by mounting an additional heatsink
mounted on the PCB. Ambient lighting applications for example need, because of the very low
output voltage (in the range of Milli-Watt), no additional heat sink, because the solder
connections are sufficient to conduct the heat from the crystal back to the LED-strip or to the
board. But if we are talking about high-power LEDs, even if they show only slightly larger
proportions compared to other diodes, it is very important to take care about their heat
development. Since they have much more power consumption and a high power density, more
heat loss will be created. High power LEDs are used primarily in floodlights, office light,
warehouses and street lighting. Without additional cooling activities, the crystal would
inevitably be destroyed within a few seconds. To overcome on this problem, the heat must be
conducted by a suitable heatsink on the PCB. The applicable cooling of the hot spots will
optimize lifetime and light-efficiency.
ASSMANN WSW components group has experience of more than 45 years in the field of
thermal management and offers, in close cooperation with the company RUTRONIK, himself a
specialist in the field of LED lighting, optimal support in the phase of development, heat sink
design, sampling right up to series production and deliveries. Special solutions and developments with alternative materials,
specific profile lengths, modern CNC machining with necessary milling work (punching, drilling,
threading), special profile shapes like hollow profiles, welded heatsink, special anodization for visual and decorative surfaces or special
packaging for manual, semi- and fully automatic configurations are available for LED application.
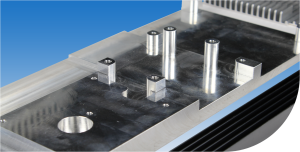
Figure 3
Figure 4
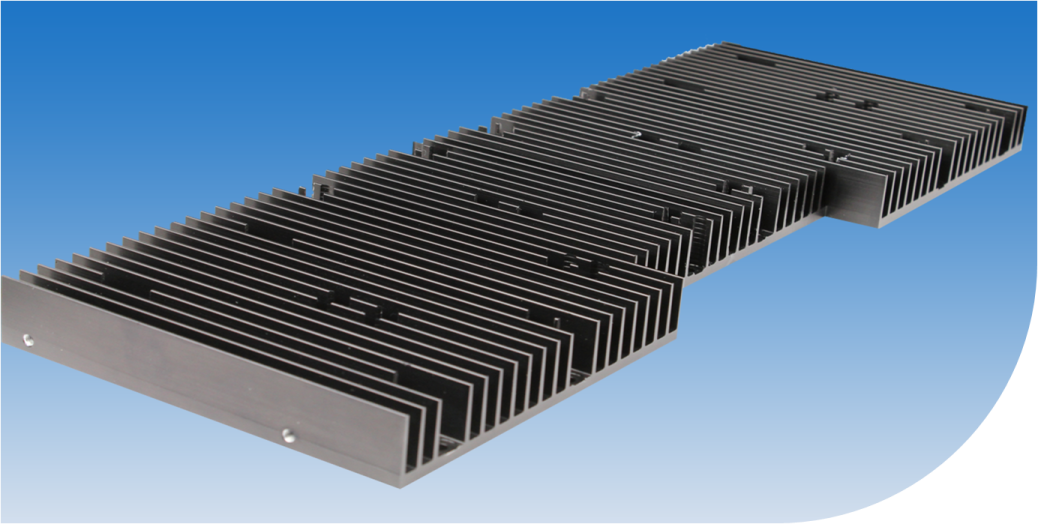
Depending on the heat level can been reached and the application itself, a wide range of
heat sinks can be used, from small finger shaped heatsinks (Figure 1) with a thermal resistance
of >16K/W), up to large extruded profile heatsinks (Rth <1K/W) (title figure). ASSMANN WSW
components group offers a large product portfolio in the thermal management market, but in
most cases, customized solutions for the individual LED-lighting systems are requested. The
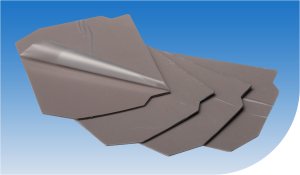
heatsink development for OEM applications begins with the construction of a forged (Figure 2),
stamped or extruded heatsink. Both, the application itself, with the available space, all other
important factors and as well as the requested heatsink shape have to be considered.
Mandatory are detailed dimensional drawings of the profile and treatment, including the
required tolerances. For very complex, customized profiles 3-D files are very helpful. The
drawings should also include the specification of the surface, whether the surface should be
free of scratches or sanded.
An additional important aspect is to minimize the thermal resistance or with other words to
maximize the heat conduction between the heat source (LED panel) and the heat sink. If the
heat transfer is not given, because of to high surface roughness, flatness or expand tolerances,
no sufficient heat exchange between the medias is given. This conduction can be improved by
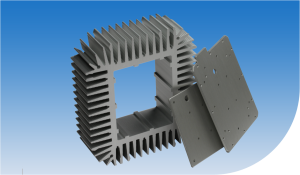
several methods, such as by mechanical CNC surface treatment (Figure 3) or using thermal
interface materials (Figure 4), such as conductive paste, adhesive or foil.
Figure 5
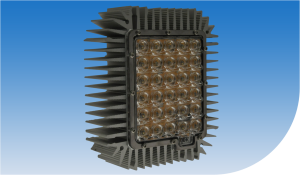
Figure 6
Figure 5 shows impressively the realization of a heatsink unit, which combines a number of
features and specifications. Hollow profiled shapes with small tolerances and fluted fin
geometry increases the surface, extruded screw rails, different front panels (for mounting the
control unit and LED board), to natural colored decorative surfaces which provide an optimized
protection to environmental influences with an anodic coating of minimum 15 μm. Figure 6
shows the completed lighting system assembled with a 30W LED panel. This unit is used to heat
dissipation of up to 60W High Power LED panels, which are used within a street lighting
application.
ASSMANN WSW provides suitable solutions for your application and is looking forward,
together with our partner RUTRONIK, to help and support your thermal challenges.